Previously, we covered the bradykinin hypothesis in COVID pulmonary pathology, where SARS-CoV-2 infected the mast cells in the lungs, releasing the signal cascade triggering bradykinin. Now let’s deal with the blood clot story - in both the cases of viral infection and vaccine injection.
COVID-19 is associated with life-threatening blood clots in the veins and arteries of not just the lungs, but also the legs (DVTs, deep vein thromboses). COVID-19 patients with lower extremity claudication had a significantly higher rate of amputation and death when compared to the uninfected cohort.
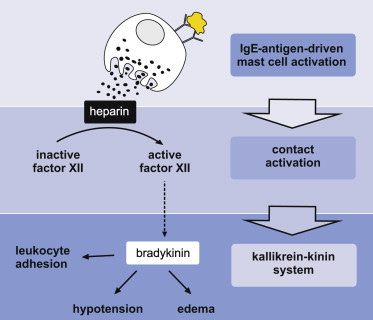
And what is its mechanism of action? Heparin released by infected mast cells activates anti-thrombin III and factor XII (Hageman Factor), which then activate the rest of the intrinsic clotting cascade. Heparin also stimulates the formation of bradykinin,
So where is the proof that the mast cells are the culprits? A University of Birmingham lab discovered that mice genetically depleted of mast cells, are protected from developing DVTs. And, these mast-cell deficient mice still could clot normally in response to injury, thus avoiding the hemorrhaging seen with standard DVT treatments such as warfarin.
In a mouse model, DVT was induced by partial ligation (stenosis) of the inferior vena cava. We demonstrated that 2 strains of mice deficient for MCs were completely protected from DVT. Adoptive transfer of in vitro differentiated MCs restored thrombosis. MCs were present in the venous wall, and the number of granule-containing MCs decreased with thrombosis. Pharmacological depletion of MCs granules or prevention of MC degranulation also reduced DVT. Basal plasma levels of von Willebrand factor and recruitment of platelets to the inferior vena cava wall after DVT induction were reduced in MC-deficient mice. Stenosis application increased plasma levels of soluble P-selectin in wild-type but not in MC-deficient mice. MC releasate elevated ICAM-1 (intercellular adhesion molecule-1) expression on HUVEC (human umbilical vein endothelial cells) in vitro. Topical application of compound 48/80, an MC secretagogue, or histamine, a Weibel–Palade body secretagogue from MCs, potentiated DVT in wild-type mice, and histamine restored thrombosis in MC-deficient animals. - T Ponomaryov et al
So logically, prescribing the well studied, relatively benign therapeutics known as mast cell stabilizers as a prophylactic to vaccination would be a prudent measure. These agents include the allergy medications cromolyn sodium and ketotifen, as well as the dietary flavonoid supplement quercetin.
In fact, instead of a donut, perhaps it would be better to give each vaccine recipient “an apple a day to keep the doctor away.” ( = great quercetin source!)
[P.S. Hops have lots of quercetin, too….]
https://biomedworks.substack.com/p/hydrogel-in-alveoli-covid-pneumonia
Radiological Society of North America. "Dangerous blood clots form in leg arteries of COVID-19 patients." ScienceDaily. ScienceDaily, 16 July 2020. https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2020/07/200716144706.html
https://medicalxpress.com/news/2011-02-heparin-key-role-player-allergy.html
University of Birmingham. "New hope to prevent dangerous blood clots found in the legs." ScienceDaily. ScienceDaily, 3 August 2017. https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2017/08/170803135051.htm
T Ponomaryov et al. “Mast Cells Granular Contents Are Crucial for Deep Vein Thrombosis in Mice” https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.117.311185
https://www.bmj.com/content/370/bmj.m2722/rr-3
https://www.livestrong.com/article/301326-foods-with-the-highest-content-of-quercetin/
Please subscribe to my free newsletter by clicking the button. Many future stories will be exclusive to only paid subscribers to BioMedWorks Newsletter: the PREMIUM CONTENT. I would be grateful if you do go on to upgrade to the paid subscription for just $5 a month or $50 a year.








https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fphar.2021.652688/full