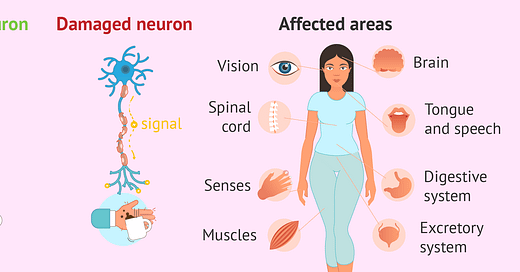
Is Vitamin B12 involved in Multiple Sclerosis?
What else are cobalamins doing? PREMIUM CONTENT subscriber access
Back in 2007-2008, I was the Chief Medical Officer and VP Clinical Development at Emisphere Technologies in New York. We developed oral formulations for drugs and peptides using carriers derived from cholesterol esters. Vitamin B12 was our Proof-of-Concept project. So, it is a compound well known to me.
Compounds with vitamin B12 activity are collectively called cobalamins. Methylcobalamin and 5-deoxyadenosylcobalamin are the metabolically active forms of vitamin B12. Two others, hydroxycobalamin and cyanocobalamin, become biologically active after being converted to methylcobalamin or 5-deoxyadenosylcobalamin.
Vitamin B12 first binds with haptocorrin when in the saliva. More vitamin B12 is derived from gastric protease and acid in the stomach. Then in the duodenum, digestive enzymes free the vitamin B12 from haptocorrin, allowing B12 to combine with Intrinsic Factor, the transport binding protein secreted by the stomach parietal cells, allowing absorption in the distal ileum via receptor-mediated endocytosis.
Vitamin B12 deficiency can occur with: deficient food (vegans), lack of Intrinsic Factor (Pernicious Anemia), GI surgery, dosing of gastric acid inhibitors (proton pump inhibitors and histamine 2-receptor antagonists) and metformin.
Keep reading with a 7-day free trial
Subscribe to BioMedWorks’ Newsletter to keep reading this post and get 7 days of free access to the full post archives.